WHAT IS PHISHING?
Phishing is a cyber crime that leverages deceptive emails, websites, and text messages to steal confidential personal and corporate information.
Victims are tricked into giving up personal information such as their credit card data, phone number, mailing address, company information, etc. This information is then used by criminals to steal the victim’s identity and commit further crimes using this stolen identity.
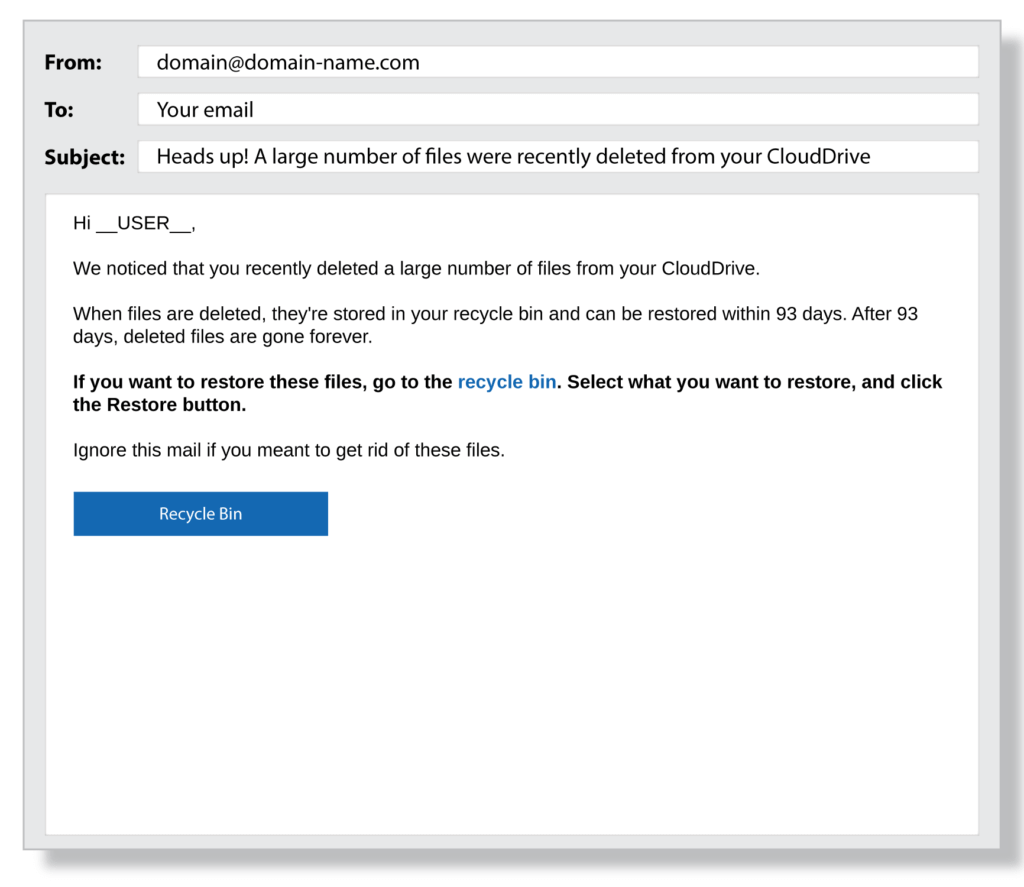
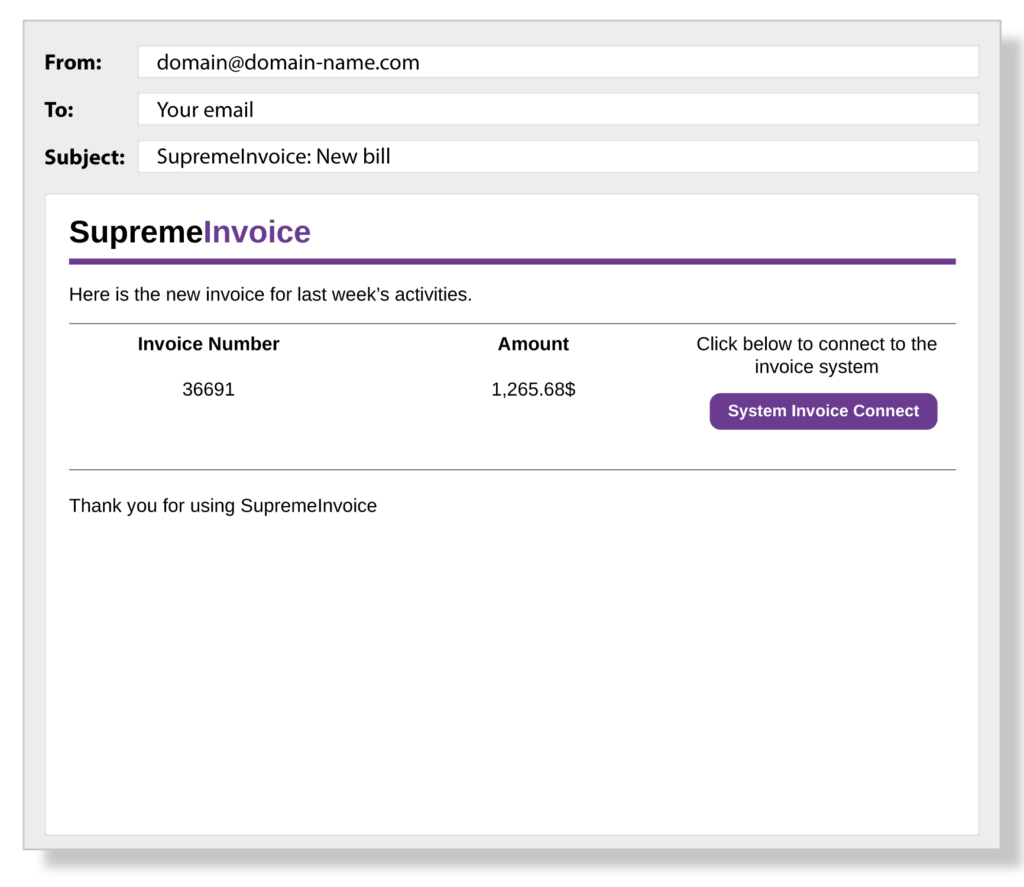
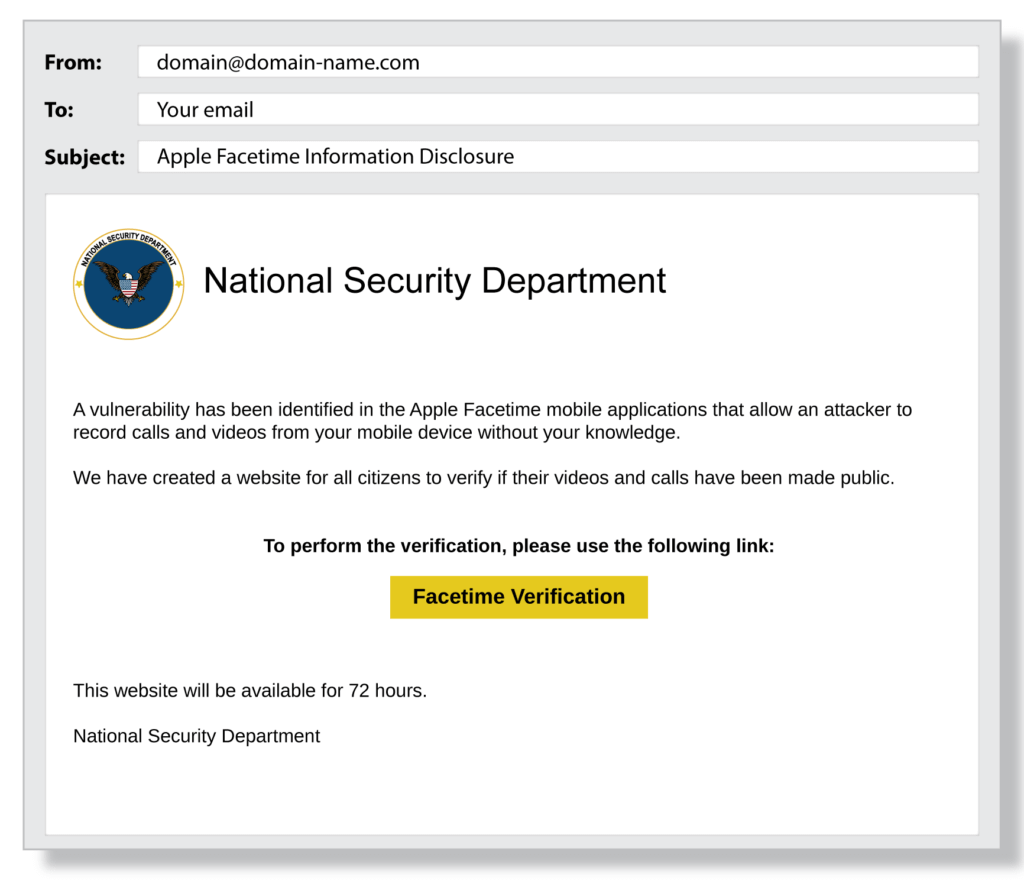
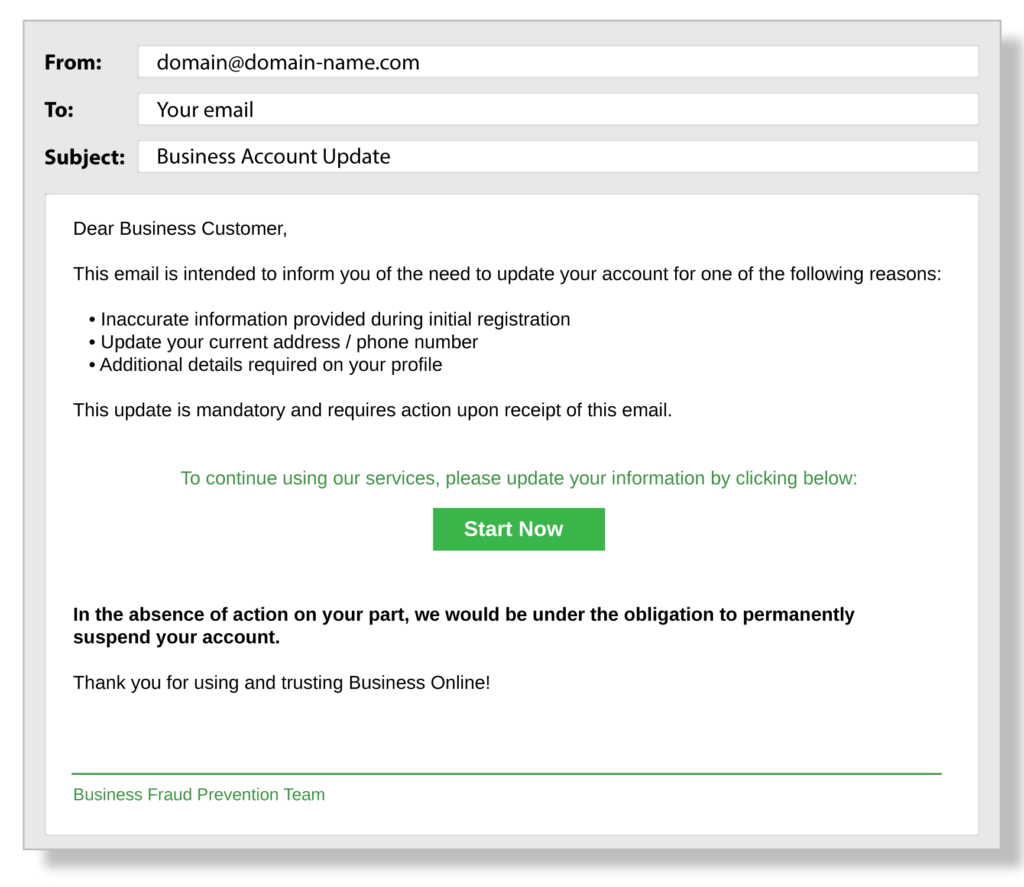
Criminals who use phishing tactics are successful because they carefully hide behind emails and websites familiar to the intended victim. For example, the email address might be administrator@ideal.org.com instead of administrator@ideal.com and urge the recipient to update their account credentials to protect them from fraud.
Phishing is a type of social engineering that criminals use to steal data, infect computers, and infiltrate company networks.